A Comprehensive Guide on Mental Illness: Types, Causes Signs and Symptoms

Mental illness is a critical issue that affects millions of people worldwide, yet it remains a topic often misunderstood and stigmatized. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into what mental illness is, explore the various types of mental illness, investigate the causes of mental illness, and discuss the common signs and symptoms of mental illness. By shedding light on this crucial subject, we aim to promote greater support, awareness, and empathy for those navigating the challenges of mental health in our center of recovery.
Understanding Mental Illness: A Closer Look
What is mental illness, exactly? Mental illness, also known as mental health disorders, refers to a wide range of conditions that impact an individual’s mood, thinking, and behavior. These disorders can vary in severity, duration, and the degree to which they interfere with daily life. It’s essential to recognize that mental illness is not a sign of weakness or a personal failing; rather, it is a legitimate health concern that requires proper care and treatment.
The Stigma Surrounding Mental Health
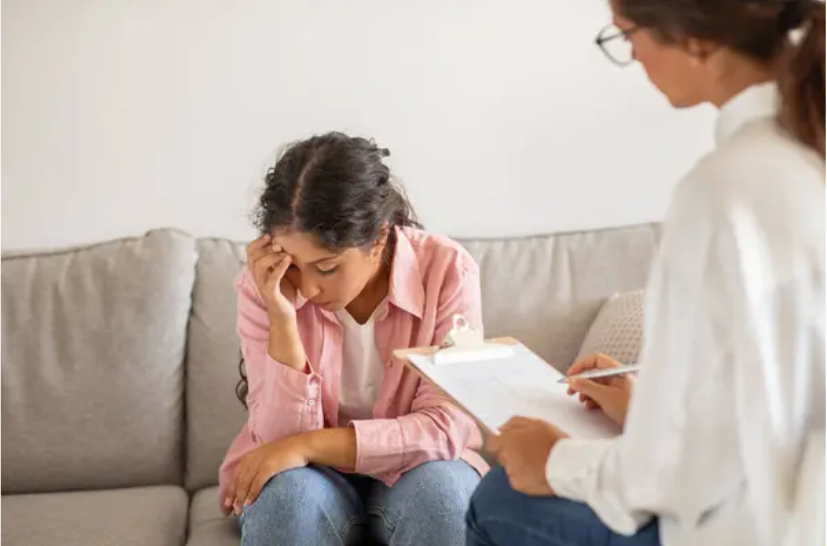
Despite the prevalence of mental illness, society often attaches a stigma to those who suffer from these conditions. This stigma can lead to discrimination, isolation, and a reluctance to seek help. Imagine feeling like you’re trapped in a dark, lonely room, with no one to turn to and no way out. That’s the reality for many people struggling with mental health issues, compounded by the fear of judgment and rejection from others.
Exploring the Types of Mental Illness

Mental illness encompasses a broad spectrum of disorders, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Let’s delve into some of the most common types of mental illness:
1. Depression: The Invisible Weight
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. It can feel like carrying an invisible weight, dragging you down and making even the simplest tasks feel insurmountable.
Symptoms of Depression
- Persistent sad or empty mood
- Loss of interest in hobbies and activities
- Changes in appetite and sleep patterns
- Fatigue and decreased energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to reach out for help. Depression is treatable, and with the right support, it is possible to find light in the darkness.
2. Anxiety Disorders: The Constant Worry
Anxiety disorders involve excessive fear, worry, and unease that can interfere with daily functioning. It’s like having a constant, nagging voice in your head, telling you that something terrible is about to happen, even when there’s no real threat.
There are several types of anxiety disorders, including:
a. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
GAD is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, relationships, and health.
b. Panic Disorder
Panic disorder involves sudden and intense episodes of fear, accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and trembling.
c. Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder is marked by an intense fear of social situations and a constant worry about being judged or embarrassed by others.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
- Excessive worry or fear
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Physical symptoms such as muscle tension, headaches, or stomachaches
If you find yourself constantly battling anxiety, know that you’re not alone and that there are effective treatments available.
3. Bipolar Disorder: The Emotional Rollercoaster
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition that causes extreme mood swings, alternating between periods of intense euphoria (mania) and severe depression. It’s like riding an emotional rollercoaster, with dizzying highs and devastating lows.
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
- Dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and activity levels
- Periods of extreme elation or irritability (mania)
- Episodes of deep depression
- Impulsive or risky behavior during manic episodes
- Changes in sleep patterns and appetite
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
Bipolar disorder can be challenging to manage, but with proper treatment and support, it is possible to find balance and stability.
4. Schizophrenia: The Blurred Line Between Reality and Delusion
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder that affects a person’s thoughts, perceptions, and behaviors. It is characterized by a disconnection from reality and can cause significant impairment in daily functioning. Imagine living in a world where the line between what’s real and what’s not is constantly blurred, and you can’t trust your own thoughts and experiences.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
- Delusions (false beliefs)
- Hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there)
- Disorganized speech and behavior
- Lack of motivation and emotional responsiveness
- Difficulty with thinking and concentration
- Social withdrawal
Schizophrenia is a complex disorder that requires ongoing treatment and support. With the right combination of medication, therapy, and social support, individuals with schizophrenia can lead fulfilling lives.
5. Eating Disorders: The Distorted Mirror
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions that involve unhealthy attitudes and behaviors related to food, weight, and body image. It’s like looking in a distorted mirror, where your perception of yourself is warped and distorted by an intense fear of gaining weight or a desire for control.
The most common types of eating disorders include:
a. Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia is characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight, leading to severe restriction of food intake and excessive weight loss.
b. Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia involves recurrent episodes of binge eating followed by purging behaviors such as self-induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives, or excessive exercise.
c. Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder is marked by regular episodes of consuming large amounts of food in a short period, often accompanied by feelings of shame and guilt.
Symptoms of Eating Disorders
- Preoccupation with food, weight, and body image
- Extreme restriction of food intake or binge eating
- Purging behaviors (vomiting, laxative abuse, excessive exercise)
- Distorted body image
- Intense fear of gaining weight
- Withdrawal from social activities
Eating disorders are serious conditions that can have severe physical and emotional consequences. If you or someone you love is struggling with an eating disorder, seeking professional help is essential for recovery.
6. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): The Lingering Echoes of Trauma
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, violent assault, or military combat. It’s like being haunted by the echoes of the trauma, long after the danger has passed.
Symptoms of PTSD
- Intrusive memories or flashbacks of the traumatic event
- Avoidance of reminders of the trauma
- Negative changes in thoughts and mood
- Hyperarousal and reactivity (feeling on edge, easily startled)
- Difficulty sleeping and concentrating
- Emotional numbness or detachment
PTSD can be a debilitating condition, but with proper treatment, including therapy and medication, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and reclaim their lives.
7. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): The Endless Loop
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by unwanted, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) that an individual feels compelled to perform to alleviate anxiety. It’s like being stuck in an endless loop of thoughts and actions, unable to break free.
Symptoms of OCD
- Persistent, unwanted thoughts or urges that cause distress
- Engaging in repetitive behaviors or mental acts to reduce anxiety
- Excessive cleaning, washing, or checking
- Arranging objects in a specific order or pattern
- Hoarding or difficulty discarding items
- Intrusive, disturbing thoughts about harm, violence, or contamination
OCD can be a challenging disorder to live with, but with the right combination of therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy) and medication, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.